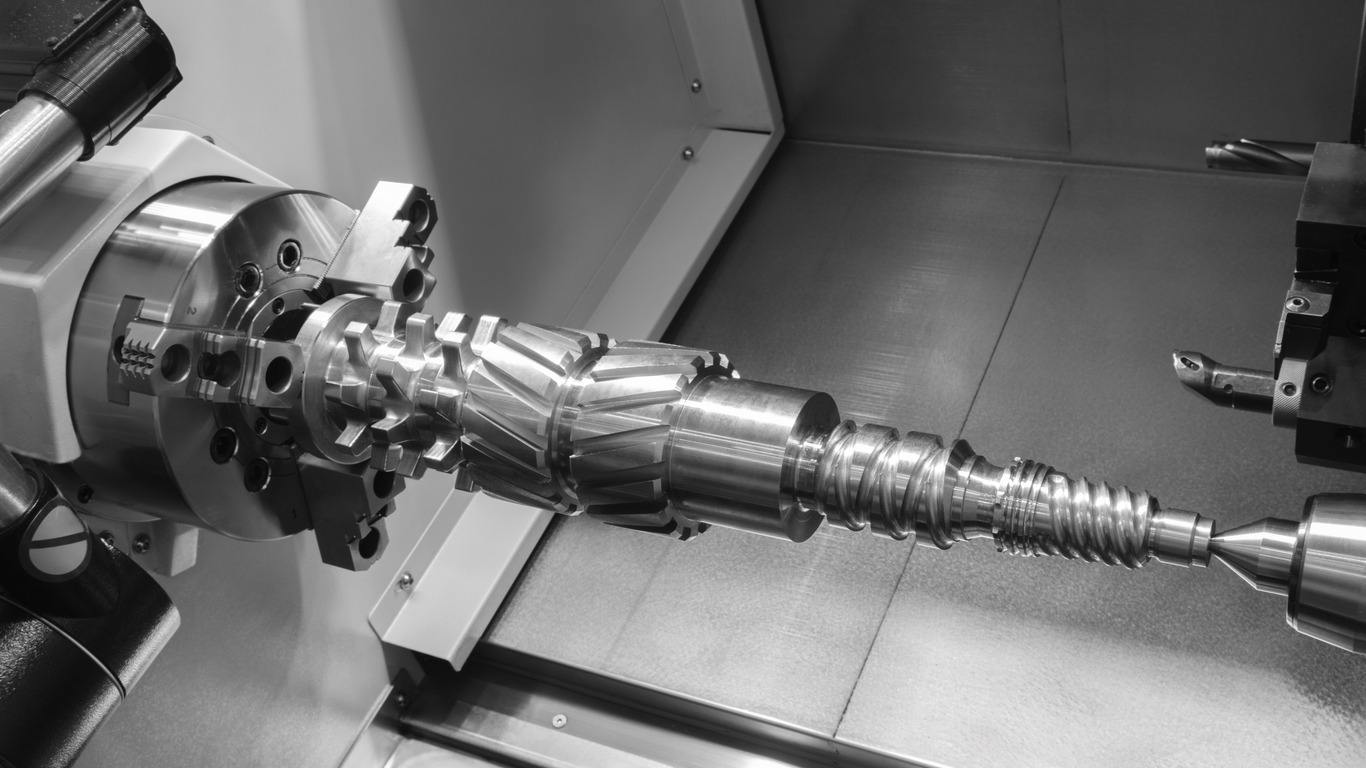
What is General Machining?
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the essential capabilities of general machining and highlight common abilities that companies often outsource for efficient production. General machining is the cornerstone of modern manufacturing, encompassing a wide range of processes that transform raw materials into precision-engineered components. From CNC milling and turning to grinding and drilling, machining plays a vital role in producing parts for various industries.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a versatile machining process where a computer-controlled machine tool removes material from a workpiece to create complex shapes and features. It utilizes rotary cutters to move along multiple axes (typically X, Y, and Z), allowing for precise cutting operations in three dimensions. CNC milling is widely used in manufacturing for its ability to produce parts with tight tolerances, intricate geometries, and smooth surface finishes.
- High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances with repeatable accuracy.
- Versatility: Capable of producing complex shapes and geometries.
- Material Compatibility: Works with metals, plastics, and composites.
CNC milling enables efficient production of prototypes, custom parts, and large-scale components with high precision and repeatability, making it essential across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
CNC Turning
CNC turning is a precision machining process where a computer-controlled lathe rotates a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create cylindrical parts. It is ideal for producing rotational components like shafts, pins, and hubs with high accuracy and efficiency.
- Efficiency: Fast production of prototypes and low to medium-volume parts.
- Rotational Parts: Ideal for cylindrical and spherical components.
- Surface Finish: Achieves smooth surface finishes for critical applications.
CNC turning offers rapid prototyping, consistent part quality, and the ability to work with various materials including metals, plastics, and composites. This technology plays a crucial role in manufacturing industries by enabling cost-effective production of complex geometries and ensuring tight tolerances for critical applications.
Grinding
Grinding is a machining process that utilizes abrasive particles to remove material from a workpiece surface. It is used to achieve precise dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes in manufacturing. Grinding operations involve rotating abrasive wheels that grind down the workpiece to the desired shape and size.
- Precision Grinding: Achieves tight tolerances and superior surface finishes.
- Tooling: Sharpening and reshaping cutting tools for enhanced performance.
- Flatness and Parallelism: Ensures parts meet strict geometric requirements.
Grinding is crucial for achieving tight tolerances, improving surface quality, and preparing parts for assembly or further processing. It is widely applied in industries such as aerospace, automotive, tooling, and precision engineering, where exacting standards for part dimensions and surface integrity are essential.
Drilling and Tapping
Drilling and tapping are fundamental machining operations used to create holes and threads in materials such as metals, plastics, and composites.
- Drilling: Involves using a rotating cutting tool called a drill bit to remove material and create cylindrical holes. Drilling operations range from simple hole creation to complex operations such as countersinking and reaming.
- Tapping: Refers to cutting threads inside a drilled hole to accommodate screws, bolts, or other fasteners. A tap is used to create internal threads that match the thread of the fastener, ensuring secure assembly.
Both drilling and tapping are essential in manufacturing processes across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. These operations require precision to achieve accurate hole diameters, depths, and thread pitches according to engineering specifications.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication involves shaping and manipulating thin sheets of metal to create various components and structures. This versatile manufacturing process encompasses cutting, bending, forming, welding, and assembling sheet metal to produce finished products.
- Cutting: Sheet metal can be cut into desired shapes and sizes using tools such as shears, lasers, or plasma cutters, depending on precision and material thickness.
- Bending and Forming: Utilizes press brakes or rollers to bend and shape sheet metal into complex geometries and configurations required for specific applications.
- Welding: Joins separate metal pieces by melting and fusing them together using various welding techniques like MIG (Metal Inert Gas) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), ensuring structural integrity.
Sheet metal fabrication is crucial across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics, where lightweight, durable, and cost-effective components are required. It offers versatility in design, precision in manufacturing, and the ability to create prototypes and custom parts efficiently.
Common Abilities Outsourced for Efficiency
- Heat Treatment
- Purpose: Enhances material properties such as hardness and strength.
- Processes: Annealing, tempering, quenching, and case hardening.
- Benefits: Improves wear resistance and durability of machined components.
- Surface Coating
- Purpose: Enhances corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Processes: Powder coating, anodizing, plating (e.g., zinc, chrome).
- Benefits: Extends component lifespan and improves appearance.
- Precision Machining of Exotic Materials
- Purpose: Common in aerospace, defense, medical, and energy industries.
- Processes: Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Benefits: Enables production of components with superior mechanical properties.
- Prototyping and Rapid Tooling
- Purpose: Allows for fast production of prototypes and tooling inserts.
- Process: Utilizes 3D printing, CNC machining, or injection molding.
- Benefits: Reduces time-to-market by accelerating design validation.
- Assembly and Sub-assembly
- Purpose: Streamlines production and reduces lead times for final products.
- Process: Combines machined parts into finished assemblies.
- Benefits: Ensures parts fit and function correctly together within desired specifications and QC standards.
Choosing a Machining Partner
When outsourcing machining capabilities, consider partnering with a provider that offers:
- Comprehensive Services: From machining to finishing and assembly.
- Quality Certifications: ISO standards for consistent quality management.
- Experience and Expertise: Track record in your industry with proven success.
Conclusion
General machining capabilities form the backbone of manufacturing, enabling the production of precise and reliable components across diverse industries. By outsourcing specialized tasks like heat treatment, surface coating, and prototyping, companies can enhance efficiency, leverage expertise, and focus on core competencies. Whether you’re developing prototypes, producing high-precision parts, or assembling complex systems, partnering with a trusted machining provider ensures you meet stringent quality standards and deliver superior products to the market.
About Corvus Engineering
At Corvus Engineering, we specialize in turning innovative ideas into reality. Our team of experienced engineers and product developers works closely with clients to design, prototype, and launch cutting-edge products. From initial concept to market launch, Corvus Engineering offers comprehensive services that include:
- Product Investigation: Research and Ideation
- Product Design and Engineering: Creating functional and aesthetically pleasing designs.
- Prototyping: Building and testing prototypes to refine your product.
- Technical Package: Provide technical specifications, detailed engineering drawings, and CAD files for manufacturing.
- Manufacturing Support: Assisting with production planning and optimization.
Partner with Corvus Engineering to bring your innovative ideas to life. Explore our website and contact us today to learn more about how we can help you create a new product that stands out in the market.